Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Sn strands under strain-applied conditions
Sn strands under strain-applied conditionsNunoya, Yoshihiko; Isono, Takaaki; Koizumi, Norikiyo; Hamada, Kazuya; Matsui, Kunihiro; Nabara, Yoshihiro; Okuno, Kiyoshi
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 18(2), p.1055 - 1058, 2008/06
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:70.64(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Japan Atomic Energy Agency has developed Nb Sn strand which can be applied to ITER TF coils. The achieved critical current density is more than 790A/mm
Sn strand which can be applied to ITER TF coils. The achieved critical current density is more than 790A/mm in bronze process strand and more than 980A/mm
in bronze process strand and more than 980A/mm in internal tin process strand under 4.2K temperature and 12T magnetic field as well as hysteresis loss of less than 770mJ/cc under
in internal tin process strand under 4.2K temperature and 12T magnetic field as well as hysteresis loss of less than 770mJ/cc under  3T cycle. Because these strand are utilized with an external strain by thermal contraction and hoop force of the coils, it is necessary to evaluate strain dependency of these strands to confirm the ITER conductor design. An apparatus to measure the strain dependency was newly developed. It has a horseshoe-shaped ring to produce uniform axial compressive or tensile strain along strand length and a strand is soldered on its outer surface. ITER TF coils will be operated under 0.77
3T cycle. Because these strand are utilized with an external strain by thermal contraction and hoop force of the coils, it is necessary to evaluate strain dependency of these strands to confirm the ITER conductor design. An apparatus to measure the strain dependency was newly developed. It has a horseshoe-shaped ring to produce uniform axial compressive or tensile strain along strand length and a strand is soldered on its outer surface. ITER TF coils will be operated under 0.77 compressive strain, magnetic field of 11.3T and temperature of 5.7K as design value. Typical obtained critical current for bronze process strand is about 92A under these designed operating conditions, which is about 20
compressive strain, magnetic field of 11.3T and temperature of 5.7K as design value. Typical obtained critical current for bronze process strand is about 92A under these designed operating conditions, which is about 20 larger than the requirement. The details of the results of strand characterization will be presented.
larger than the requirement. The details of the results of strand characterization will be presented.
Kizu, Kaname; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Yoshida, Kiyoshi; Edaya, Masahiro; Ichige, Toshikatsu*; Tamai, Hiroshi; Matsukawa, Makoto; della Corte, A.*; Di Zenobio, A.*; Muzzi, L.*; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 18(2), p.212 - 215, 2008/06
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:67.07(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)The maximum magnetic field and maximum current of CS and EF coils is 9 T, 20 kA and 6.2 T, 21 kA, respectively. The conductor for CS is Nb Sn CIC conductor with JK2LB conduit. On the other hand, EF coil conductors are NbTi CIC conductor with SS316LN conduit. In order to reduce the pressure drop and to raise the temperature margin against large AC loss and nuclear heating, central spiral is introduced inside cable. The Tcs margin and stability analyses of the CS and EF coils are performed by using the one-dimensional fluid analysis code with transient heat loads. These coils have enough high Tcs and stability margin against the operational scenario.
Sn CIC conductor with JK2LB conduit. On the other hand, EF coil conductors are NbTi CIC conductor with SS316LN conduit. In order to reduce the pressure drop and to raise the temperature margin against large AC loss and nuclear heating, central spiral is introduced inside cable. The Tcs margin and stability analyses of the CS and EF coils are performed by using the one-dimensional fluid analysis code with transient heat loads. These coils have enough high Tcs and stability margin against the operational scenario.
Pizzuto, A.*; Semeraro, L.*; Zani, L.*; Bayetti, P.*; Cucchiaro, A.*; Decool, P.*; della Corte, A.*; Di Zenobio, A.*; Dolgetta, N.*; Duchateau, J. L.*; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 18(2), p.505 - 508, 2008/06
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:64.34(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)The Broader Approach agreement between Europe and Japan includes the construction of a fully superconducting tokamak, the JT-60 Super Advanced (JT-60SA), as a satellite experiment to ITER. Toroidal field (TF) magnet which consists of 18 D-shaped coils will be provided to Japan by EU. TF coil main constituents are conductor, winding pack, joints, casing and current leads. The design criteria about conductor and structure were discussed between JA and EU adopted to fulfill the machine requirements. The results of the analyses performed by EU and JA to define and assess the TF magnet system conceptual design, are reported and commented.
Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Suzuki, Yutaka; Kizu, Kaname; Yoshida, Kiyoshi; Tamai, Hiroshi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Dolgetta, N.*; Portafaix, C.*; Zani, L.*; Pizzuto, A.*
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 18(2), p.208 - 211, 2008/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:42.45(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Magnet system in JT-60SA consists of 18 toroidal field coils, 7 plasma equilibrium field (EF) coils, and central solenoid (CS) that has 4 modules of solenoids. Mechanical design of EF coils and CS is optimized in order to obtain the broad operational space of plasmas that are double-null plasma with high plasma current for high performance operation and ITER-like configuration with IP=3.5MA for ITER-relevant experiment. In the former design, called NCT, divertor coil (EF4) is made of Nb Sn conductor, as well as CS conductor. However, it is clear that 6.2T of Bmax is significant to operate ITER-like plasma. Therefore, material of cable for EF4 conductor is changed into NbTi, so that this contributes to cost reduction. Regarding CS design, material of conduit is changed into JK2LB in order to simplify the structure of pre-compression. Stress analysis for support structure and winding pack of EF coils and CS is currently carried out. In the case where the vertical unbalance force of CS is largest in the designed plasma operation, peak stress of conduit is less than fatigue limit in 18,000 cycles that is designed number of plasma shot in JT-60SA. This result shows the recent design of CS conductor has significant mechanical strength.
Sn conductor, as well as CS conductor. However, it is clear that 6.2T of Bmax is significant to operate ITER-like plasma. Therefore, material of cable for EF4 conductor is changed into NbTi, so that this contributes to cost reduction. Regarding CS design, material of conduit is changed into JK2LB in order to simplify the structure of pre-compression. Stress analysis for support structure and winding pack of EF coils and CS is currently carried out. In the case where the vertical unbalance force of CS is largest in the designed plasma operation, peak stress of conduit is less than fatigue limit in 18,000 cycles that is designed number of plasma shot in JT-60SA. This result shows the recent design of CS conductor has significant mechanical strength.
Yoshida, Kiyoshi; Kizu, Kaname; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Tamai, Hiroshi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; della Corte, A.*; Muzzi, L.*; Turt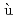 , S.*; Di Zenobio, A.*; et al.
, S.*; Di Zenobio, A.*; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 18(2), p.441 - 446, 2008/06
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:71.77(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)The upgrade of JT-60U magnet system to superconducting coils (JT-60SA) has been decided by both parties of Japan and EU in the framework of the Broader Approach agreement. The magnet system for JT-60SA consists of 18 toroidal field (TF) coils, a central solenoid (CS) with four modules, seven equilibrium field (EF) coils. TF case encloses the winding pack and is the main structural component. CS consists of four winding pack modules with its pre-load structure. Seven EF coils are attached to the TF coil cases through supports which include flexible plates. Since CS modules are operated at high magnetic field, Nb Sn superconductor is used. While NbTi superconductor is used in TF coils and EF coils. The magnet system has large heat load from nuclear heating by DD fusion and large AC loss from control actions. This paper descries the technical requirements, the operational interface and the conceptual design of the superconducting magnet system for JT-60SA.
Sn superconductor is used. While NbTi superconductor is used in TF coils and EF coils. The magnet system has large heat load from nuclear heating by DD fusion and large AC loss from control actions. This paper descries the technical requirements, the operational interface and the conceptual design of the superconducting magnet system for JT-60SA.
Koizumi, Norikiyo; Nakajima, Hideo; Matsui, Kunihiro; Isono, Takaaki; Okuno, Kiyoshi; Takayanagi, Tadatoshi*; Kuno, Kazuo*; Senda, Ikuo*
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 18(2), p.475 - 478, 2008/06
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:61.02(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)ITER-TF coil is scaled up by about 3 times from TFMC, which was developed in ITER EDA and successfully tested in EU. New technical issues are initiated because of the scale-up. The major issues are feasibilities of high accuracy automatic winding, precise prediction of conductor elongation and/or shrinkage after heat treatment to transfer the conductor in narrow grove of radial plate. It is also necessary to develop insulation system, whose radiation resistance is enough to sustain irradiation in ITER TF coil and which enable vacuum impregnation in suitable duration, such as 24 h. The authors therefore develop one of major parts of automatic winding machine, bending roller head, and optimize TF winding shape to enable successive winding. In addition, the elongation of the TF conductors was evaluated in  200 ppm after the heat treatment. Moreover, impregnation test of the conductor was performed. The test results indicate that it will take a several ten hours to impregnate TF double-pancake by the method developed in EDA.
200 ppm after the heat treatment. Moreover, impregnation test of the conductor was performed. The test results indicate that it will take a several ten hours to impregnate TF double-pancake by the method developed in EDA.
 Sn conductors for ITER toroidal field coils
Sn conductors for ITER toroidal field coilsTakahashi, Yoshikazu; Isono, Takaaki; Koizumi, Norikiyo; Nunoya, Yoshihiko; Matsui, Kunihiro; Nabara, Yoshihiro; Hemmi, Tsutomu; Oshikiri, Masayuki; Uno, Yasuhiro*; Okuno, Kiyoshi; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 18(2), p.471 - 474, 2008/06
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:62.77(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)The ITER TF coil system consists of 18 D-shape coils. The operating current and the maximum field are 68 kA and 11.8 T, respectively. A Nb Sn cable-in-conduit conductor with a central channel is used, with a unit length of about 380 m. A cable consists of 900 Nb
Sn cable-in-conduit conductor with a central channel is used, with a unit length of about 380 m. A cable consists of 900 Nb Sn strands and 522 Cu strands with a diameter of 0.82 mm. Superconducting performance of full-size conductors manufactured was measured at the operating condition of the TF coils with the maximum field. The strands made by bronze and internal-Sn methods were used for the sample conductors with a void fraction of 29% and 33%, respectively. The measured current sharing temperatures Tcs are 6.5-6.7K for the bronze route method and 5.7-5.9K for the internal-Sn method. The Tcs of the conductor with small void fraction is relatively higher with 0.1-0.2K than that with large void fraction. It is confirmed that Tcs of both strands is higher than the design value (5.7K). It is shown from the results that the strain on the conductor, estimated by the strand data, is about -0.7%. This value seems to be reasonable.
Sn strands and 522 Cu strands with a diameter of 0.82 mm. Superconducting performance of full-size conductors manufactured was measured at the operating condition of the TF coils with the maximum field. The strands made by bronze and internal-Sn methods were used for the sample conductors with a void fraction of 29% and 33%, respectively. The measured current sharing temperatures Tcs are 6.5-6.7K for the bronze route method and 5.7-5.9K for the internal-Sn method. The Tcs of the conductor with small void fraction is relatively higher with 0.1-0.2K than that with large void fraction. It is confirmed that Tcs of both strands is higher than the design value (5.7K). It is shown from the results that the strain on the conductor, estimated by the strand data, is about -0.7%. This value seems to be reasonable.
Zani, L.*; Pizzuto, A.*; Semeraro, L.*; Ciazynski, D.*; Cucchiaro, A.*; Decool, P.*; della Corte, A.*; Di Zenobio, A.*; Dolgetta, N.*; Duchateau, J. L.*; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 18(2), p.216 - 219, 2008/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:30.89(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)The upgrade of JT-60U to JT-60 Super Advanced (JT-60SA), a fully superconducting tokamak, will be performed in the framework of the Broader Approach (BA) agreement between Europe (EU) and Japan. In particular, the Toroidal Field (TF) system, which includes 18 coils, is foreseen to be procured by France, Italy and Germany. This work covers activities from design and manufacturing to shipping to Japan. The present paper is mainly devoted to the analyses that lead to the conductor design and to the technical specifications of the joints for the JT-60SA TF coils. The conductor geometry is described, which is derived from Cable-In-Conduit concept and adapted to the actual JT-60SA tokamak operating conditions, principally the ITER-like scenario. The reported simulations and calculations are particularly dealing with the stability analysis and the power deposition during normal and off-normal conditions (AC losses, nuclear heating). The final conductor solution was selected through a trade-off between scientific approach and industrial technical orientation. Besides, the TF system connections layout is shown, derived from the industrially assessed twin-box concept, together with the associated thermo-hydraulic calculations ensuring a proper temperature margin.
 Sn strand in CIC conductor
Sn strand in CIC conductorMurakami, Haruyuki*; Ishiyama, Atsushi*; Ueda, Hiroshi*; Koizumi, Norikiyo; Okuno, Kiyoshi
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 18(2), p.1051 - 1054, 2008/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:20.19(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Critical current was degraded by periodic transverse load in a CICC. A simulation code was developed to study mechanism of this degradation in details. The simulation results were compared with results of experiment in which single strand was periodically bent. Since the test results could not be simulated well in the previous work, the authors carried out improvements of the model, such as use of electro-plastic model and detail evaluation of conductance among filaments. By these improvements the agreement between the simulation and experiment can be modified. This results in verifying validity of our code. Using our code, the general dependence of the critical current degradation on strand configuration, such as barrier thickness, RRR of bronze and twist pitch of filament, are evaluated. The results show barrier thickness affects critical current performance because of its large bending rigidity. On the other hand, RRR of bronze and twist pitch of filament hardly affects critical current performance.
Kamiya, Junichiro; Kinsho, Michikazu; Kuramochi, Masaya; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Takeda, Osamu; Ueno, Tomoaki; Watanabe, Masao; Yamamoto, Kazami; Yamazaki, Yoshio; Yoshimoto, Masahiro
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 18(2), p.293 - 296, 2008/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:26.1(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)The kicker magnets are installed in the extraction section in the Rapid Cycling Synchrotron (RCS) of J-PARC and they extract a proton beam accelerated up to 3 GeV. We performed the mapping in the air applying one third of operational voltage after checking linear dependence of magnetic field with excitation current. A short search coil with the 3-axias stage was used to measure the magnetic field distribution. The results showed that the distribution in the medium plane of the same type of kicker magnet is in good agreement with each other. The excitation test with the operational charging voltage of 60 kV was also performed in a vacuum. At the first stage, we were bothered by the electric breakdown. It was noticed that the reduction of outgassing rate by baking is very effective to suppress the discharge. Pressure and mass spectrum measured during the excitation test showed that the excitation of the kicker magnet has conditioning effect.
Tatsumoto, Hideki; Shirai, Yasuyuki*; Hata, Koichi*; Kato, Takashi; Aso, Tomokazu; Otsu, Kiichi; Shiotsu, Masahiro*
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 18(2), p.1483 - 1486, 2008/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:34.99(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)The knowledge of forced flow heat transfer of liquid hydrogen is important for cooling design of hydrogen moderator system and HTS superconducting magnets such as MgB magnet. The use of a CFD code is necessary to understand the heat transport phenomena in the practical cooling channel of the magnets. As a first step of the study, forced flow heat transfer of liquid nitrogen in a horizontal tube, instead of liquid hydrogen, was analyzed in this work by using a CFD code. The solutions were compared with the authors' experimental data under the corresponding conditions. The solutions obtained by using the low Reynolds number
magnet. The use of a CFD code is necessary to understand the heat transport phenomena in the practical cooling channel of the magnets. As a first step of the study, forced flow heat transfer of liquid nitrogen in a horizontal tube, instead of liquid hydrogen, was analyzed in this work by using a CFD code. The solutions were compared with the authors' experimental data under the corresponding conditions. The solutions obtained by using the low Reynolds number 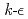 model as a turbulent model agreed well with the experimental data for the Reynolds numbers (
model as a turbulent model agreed well with the experimental data for the Reynolds numbers (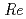 ) higher than 1
) higher than 1
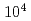 . For
. For 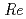
 1
1
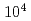 , the solutions become lower than the experimental data. The heat transport mechanism in the horizontal tube was also clarified by the analyses.
, the solutions become lower than the experimental data. The heat transport mechanism in the horizontal tube was also clarified by the analyses.
Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Kanazawa, Kenichiro; Ueno, Tomoaki; Someya, Hirohiko*; Harada, Hiroyuki*; Irie, Yoshiro; Kinsho, Michikazu; Yamazaki, Yoshishige; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Kamiya, Junichiro; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 18(2), p.306 - 309, 2008/06
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:50.78(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)The four shift bump magnets (BUHS01-04) of the 3-GeV RCS in J-PARC, which are located at the long straight section, produce a fixed main bump orbit to merge the injection beam into the circulating beam. They are realized with four magnets connected in series to form the accurate closed bump orbit. However, the total integrated magnetic field of the four magnets is not zero because of the magnetic field interferences between the shift bump magnet and the adjacent quadrupole magnet (Q magnet). In order to decrease the imbalance of the integrated magnetic field, 0.3mm insulators were inserted at the median plane of the return yoke of the second and third shift bump magnets (BUHS02 and BUHS03). The integrated field has been decreased from 2358.0 Gauss-cm to -71.6 Gauss-cm, resulting in the closed orbit distortion of the beam to be decreases from 6.0 mm to less than 1.0 mm.
Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Kanazawa, Kenichiro; Ueno, Tomoaki; Someya, Hirohiko*; Harada, Hiroyuki*; Irie, Yoshiro; Kinsho, Michikazu; Yamazaki, Yoshishige; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Kamiya, Junichiro; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 18(2), p.310 - 313, 2008/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:20.19(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)The beam painting injection system of the 3-GeV RCS in J-PARC, which realizes the uniform beam distributions in the ring, consists of four horizontal paint bump magnets and two vertical paint magnets. Each paint bump magnet power supply is required to excite the current with high accuracy that varies from 17.6 kA to zero during 0.5 msec. The IGBT chopper units, the switching frequency of which is 50 kHz each, are multiple connected to achieve the effective carrier frequency of 600 kHz. The output accuracy is then achieved to be less than 1 %. The measurements of the magnetic field with the actual current waveform were performed and the good performance was confirmed.
Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Ueno, Tomoaki; Togashi, Tomohito; Takeda, Osamu; Kanazawa, Kenichiro; Watanabe, Masao; Yamazaki, Yoshio; Kamiya, Junichiro; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Kuramochi, Masaya; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 18(2), p.297 - 300, 2008/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:30.89(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Ueno, Tomoaki; Togashi, Tomohito; Toyokawa, Ryoji; Takeda, Osamu; Watanabe, Masao; Yamazaki, Yoshio; Yamamoto, Kazami; Kamiya, Junichiro; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 18(2), p.301 - 305, 2008/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.89(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)